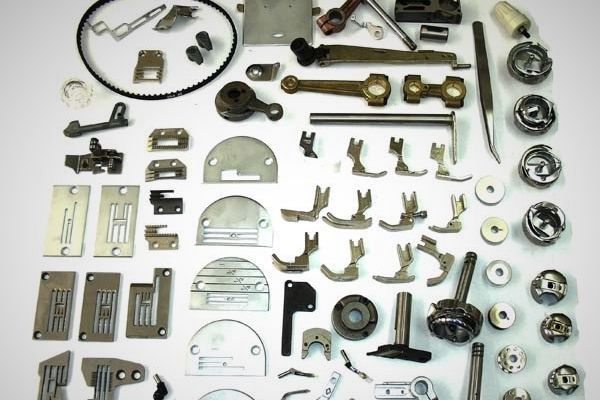
19 Different Parts of a Sewing Machine (Names and Functions)
The sewing machine is an integral part of home life. It is there for years helping you to repair torn pants, blouses, uniforms, and even wedding dresses. Learning the different parts of the sewing machine should help you use it better and know what needs to be done to fix it when something goes wrong.
One part of the sewing machine that won’t be part of this list is the sewing cabinet. This cabinet or table can give you a great place to do your sewing while protecting your machine from harm. Of all the features, this may be the best one.
To find out all the parts on a sewing machine in addition to that one, just continue to read our article. We give you their names and their functions so you can know your sewing machine like the back of your hand.
Sewing Machine Parts Name List
It is a bit of a long list, so sit back, get a cup of coffee and take your time reading. There is no need to rush through reading this list. Just enjoy and spend a few moments learning about your sewing machine.
We should say that not all sewing machines come with every part listed here. Some may be basic machines that have fewer parts to them and cost you a lot less.
1. Spool Pin

- Thread usually comes on a spool. That is the wooden thread holder you buy in the store. The spool pin holds the spool of thread for you making it easier for you to thread your machine and keep the thread coming as you want it to. Read about the spool pin felt.
2. Bobbin Binder Spindle

- A bobbin is a little cylinder that may come with or without flanges. It holds the thread that is wound around it. The spindle is where the bobbin is placed during winding.
3. Bobbin Winder Stopper

- The bobbin is only so large. It cannot always hold the amount of thread you want to put on it. This part stops the bobbin from collecting thread when it has reached full capacity.
4. Stitch Width Dial

- On many newer sewing machines, you get a variety of stitch options to use. The purpose of this part is to control the zig-zag stitch option while you are busy concentrating on your sewing.
5. Pattern Selector Dial

- This little dial allows you to select one stitch pattern out of the many that come built into your sewing machine. You just turn the dial to get the pattern that you want on your clothes and other fabrics you want to mend or create.
6. Hand Wheel

- This is the manual needle control which raises or lowers the needle. It is usually located at the right-hand side of the machine. It shouldn’t be that hard to turn.
7. Stitch Length Dial

- More recent sewing machines may have this part attached to them. Its purpose is to control the length of your selected stitch. This helps you stay in control of your sewing duties and make sure you get what you want and need.
8. Reverse Stitch Lever

- Once you push this lever, you get to sew in the opposite direction. This function makes your sewing a little easier and faster to do because you can go forward or in reverse when you need to.
9. Power Switch

- You already know what this switch does. The key to using it is to make sure you turned your sewing machine off before you walk away. Also, it should be located at the right side of your machine.
10. Bobbin Winder Thread Guide

- When you activate this part on your sewing machine, you are guiding the thread towards the bobbin/ This makes winding your thread up a little easier and should prevent twists, tangles or caught thread.
11. Thread Tension Dial

- Tension is important when you do your sewing. Too loose can cause you problems and too much tension could snap your thread and make sewing more time consuming as you have to re-thread the machine. This little part simply controls the tension on the thread so be careful when you use it.
12. Thread Take-Up Lever

- Your top thread passes through this part as you do your sewing. The lever moves up and down with your needle so do not be alarmed that it is constantly moving.
13. Needle Clamp Screw

- Needles do not stay in place by themselves. It would be nice if they did. You need this part to hold your needle where it is supposed to be. It also makes sure your needle is secure as it moves.
14. Presser Foot

- This is the part that holds your fabric so it doe snot slip all over the place while you are working. Controlling your fabric is important while you do your sewing.
15. Bobbin Cover

- Your sewing machine parts do need some protection to keep them in top working order and to help then last you for years. This is the job of the bobbin cover. It protects the bobbin as it covers it.
16. Bobbin Cover Release Button

- Also, you need access to your bobbin when it its filled with thread or there is a problem. This release button helps you to remove the bobbin cover so you have complete access to your bobbin.
17. Feed Dog

- It is an interesting name, but it has a very straightforward function., This part feeds your fabric through the sewing machine while you are sewing. This helps you concentrate on other sewing needs as you work.
18. Needle

- Another self-explanatory label that tells you everything you need to know. The needle is an integral part of the sewing machine and without it, the other parts cannot do their job.
19. Needle Plate

- This part is located right under the needle and an under the presser foot. Its job is to help move the fabric forward as you sew. It may help help push the fabric back when you use the reverse mode on your sewing machine.
Parts of Hand Sewing Machine
The hand sewing machine model is operated by either a hand wheel or a foot pedal. The pedal is often called the treadle and it powers your sewing machine while you move your feet.
There are a variety of versions of hand sewing machine units so they may or may not have all the parts we list here. There also may be some duplication of the list above. That is due to the fact that there are basic parts that go on all models of sewing machines, no matter how old or new.
1. Hand Wheel
- This is operated by hand and you pull or push it to make your needle go up or down.
2. Foot Pedal or Treadle
- Instead of using your right hand, you use your feet. All you do is push on the pedal to make your sewing machine work like it should. You may get some good exercise in with this option.
3. Belts
- These belts are like any belt that operates machinery. Without them the hand wheel or foot pedal could not move the needle or other active parts on your machine.
4. Bobbin
- The same function as above and it collects your thread as you work.
5. Bobbin Case
- This holds your bobbin keeping it safe from damage while it moves to wind your thread.
6. Bobbin Winder
- It makes sure as you wind your thread, the bobbin does not collect too much.
7. Needle Plate
- Does the same job on hand models as it doe son modern sewing machines. It helps move the fabric forward as you sew.
8. Shuttle
- This little part works with your bobbin to make sure you keep the thread from tangling and keep it moving correctly.
9. Needles
- Again, the most important part of the sewing machine. You may or may not be able to sharpen them. It all depends if they get bent or not.
Overlock Sewing Machine Parts and Functions
This machine will have similar parts as the two listed above. We shall try to highlight only those that are unique on this machine or not mentioned in the above lists.
1. Lubricating Mechanisms
- This brings the oil and other lubricating materials to your moving sewing machine parts.
2. Needle Guard
- Does just what it says. It guards the needle just in case there is a problem and too much fabric, or some other item gets to close to the needle.
3. Loopers
- This may help lop your thread to keep it from getting tangled or in your way.
4. Thread Guide and Takeup
- This part guides your thread keeping it on the right path it is to take as it moves. Then it helps take up the thread when it is needed to be done.
5. Knives or Thread Cutter
- What this part does is cut the thread where you want it cut when you are done sewing that stitch or pattern. It is usually the last part you use when you have completed your sewing task.
6. Gaskets
- These help hold the metal parts together and keeps them from creating too much heat or friction.
7. Bushings & Bearings
- These little parts make sure all moving parts function as they should. You should keep an eye on them in case there is a problem. They do tend to wear out after a while.
8. Springs
- Another needed part to help your overlock machine to perform at peak levels all the time. They are also a vulnerable part that may bend or break if you are not careful.
9. Screws, Washers and Nuts
- Vital hardware that holds your overlock machine together. You may need to loosen or tighten these from time to time as they may come loose or you need to remove them to fix other parts.
10. Needle Clamps
- This part is the same as mentioned above. It holds your needle where it belongs and make sure you can get your sewing done without any trouble from the needle.
A Little History of The Sewing Machine

The device was first invented in 1790 by an Englishman named Thomas Saint. The original patented sewing machine may have been a combined effort relying on previous inventor’s work, ideas and innovations.
But he is credited with bringing the sewing machine into existence. His machine was capable of only producing a chain stitch.
In 1832 Walter Hunt, in New York, added his own ideas to the sewing machine. He put the lock stitch and eye needle on his version. This is how the sewing machine developed over time. People kept adding their own innovations to improve the machine and make sewing life better and easier.
Another example of this was done in 1845 by Elias Howe who placed the curved eye pointed needle and an under thread shuttle on his model. He was also able to increase the speed of the sewing machine to 250 stitches per minute.
When 1846 came along, Isacc Singer developed the straight needle and made the machine sew continuously. After that, and you should know the Singer brand name, the rest is history as growing technology helped create better sewing machines until we have the most recent modern versions which can do just about everything.
Some Final Words
- Understanding your sewing machine and its different parts help you use your version a lot better. Knowing how it works speeds up the threading, and other functions you need to do before you start.
- There will always be the same basic parts no matter which version you own and use. It is the innovations that you need to be most aware of since they help you create some very exotic and great looking stitches as well as patterns.
- Know your machine so your sewing talent can grow and be even better than before.